Nuclear Spin
Nuclear spin is a quantum mechanical property of nuclei. As a nucleus has charge and spins it will generate a magnetic field. The spin of a nucleus depends on the combination of protons and neutrons with the nucleus.
Nuclei with an odd mass number (e.g. 1H, 13C, 15N, 17O, 19F, 31P) have fractional spin ( ½, 3⁄2, etc.).
Nuclei with and even mass number but an odd number of protons and electrons (e.g. 2H, 14N) have integer spin (1, 2, etc.).
Nuclei with and even number of both protons and electrons ( 12C, 16O) have zero spin and will not produce NMR spectra.
NMR active nuclei have charge and rotate giving them a magnetic moment.
Nuclei of spin ½ have a spherical charge distribution and will orientate either with or against the applied magnetic field.
Low and high energy states. The lower energy state is slightly more populated than the high energy state (Boltzmann distribution).
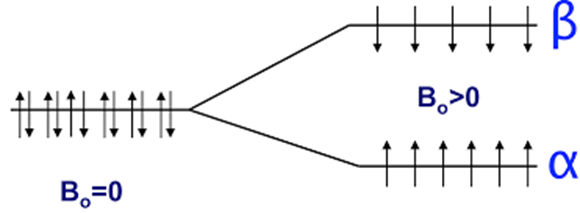
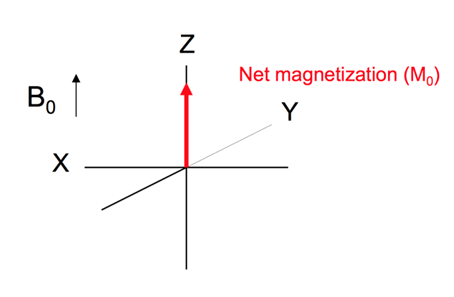
The resulting net magnetisation of the nuclei lies in the direction of the applied magnetic field.
Previous: Principles of NMR
